Sampling objects in the 3D Front Dataset¶
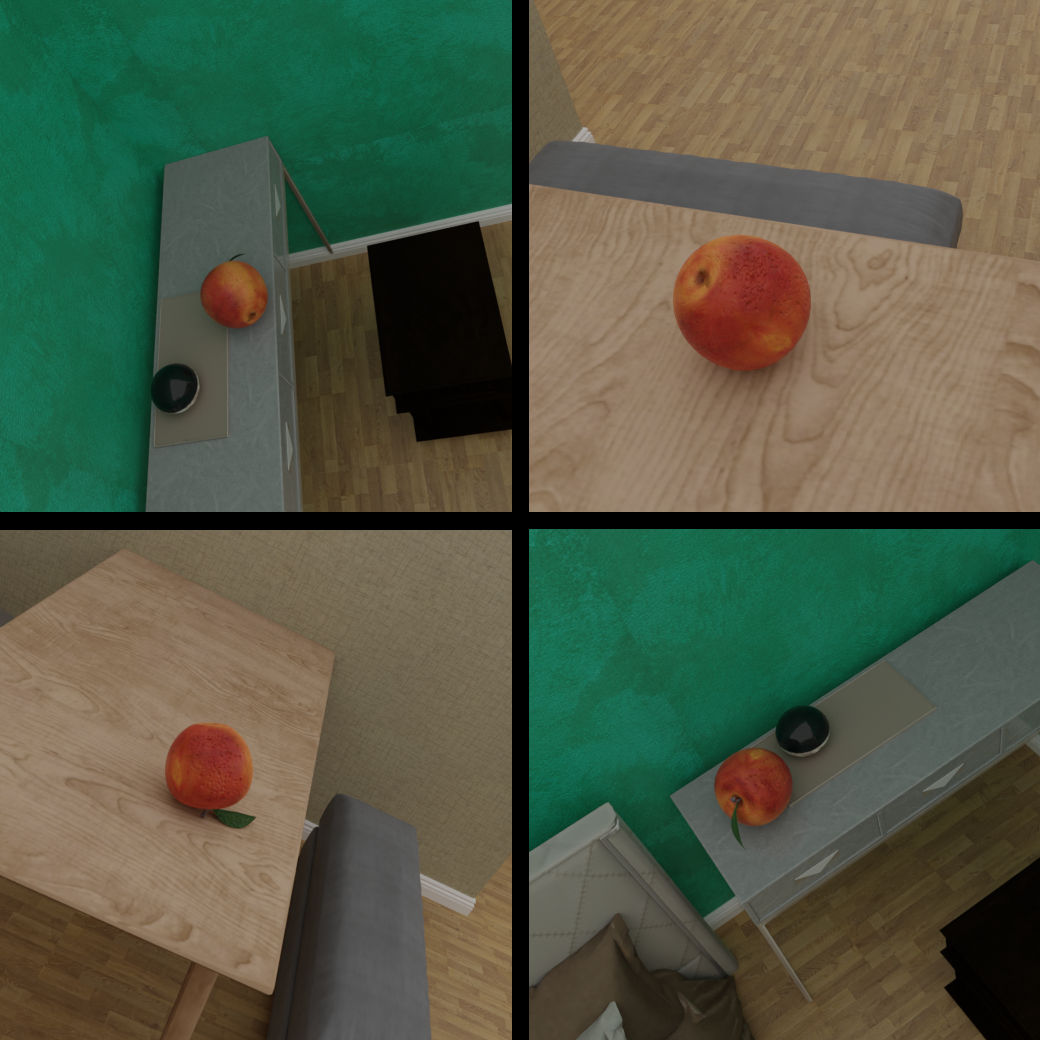
In this example, we explain to you how to sample specific objects in the 3D-Front Dataset with the BlenderProc pipeline. What’s special is, that we select the surface object beforehand and that the sampled object is placed directly on the surface of a table for example. This is an advanced example, make sure that you have executed the basic examples before proceeding to this one.
Usage¶
Execute in the BlenderProc main directory:
blenderproc run examples/datasets/front_3d_object_sampling/main.py {PATH_TO_3D-Front-Json-File} {PATH_TO_3D-Future} {PATH_TO_3D-Front-texture} {PATH_TO_3d_object} examples/datasets/front_3d/output
examples/datasets/front_3d/main.py: path to the python file with pipeline configuration.- PATH_TO_3D-Front-Json-File: path to the 3D-Front json file. For the example pictures we used: “036bc96c-419d-4a43-812e-1e533d95dfd3.json”
PATH_TO_3D-Future: path to the folder where all 3D-Future objects are storedPATH_TO_3D-Front-texture: path to the folder where all 3D-Front textures are stored- PATH_TO_3D-Object: path to the downloaded 3D object, get it [here](https://www.cgtrader.com/free-3d-models/food/fruit/apple-1)
examples/datasets/front_3d_object_sampling/output: path to the output directory
Visualization¶
Visualize the generated data:
blenderproc vis hdf5 examples/datasets/front_3d_object_sampling/output/0.hdf5
Steps¶
- Loads the
.jsonfile:bproc.loader.load_front3d. It creates the rooms and also adds emission shaders to the ceiling and lamps. - Select the surfaces, where the objects should be sampled on:
bproc.object.slice_faces_with_normals(). - Load the object, which should be sampled on the surface:
bproc.loader.load_blend(). - Sample the object on the surface:
bproc.object.sample_poses_on_surface(). - Run the physics simulation:
bproc.object.simulate_physics_and_fix_final_poses. - Check if the objects are still on the surface.
- Adds camera pose to the scene:
bproc.camera.add_camera_pose(). - Renders all set camera poses:
bproc.renderer.render(). - Writes the output to .hdf5 containers:
bproc.writer.write_hdf5().
Python file (main.py)¶
Front3DObjectSelection¶
# Select the objects, where other objects should be sampled on
for obj in room_objs:
if "table" in obj.get_name().lower() or "desk" in obj.get_name().lower():
left_objects.append(obj)
for obj in left_objects:
# The loop starts with and UndoAfterExecution in order to restore the camera positions for each object
with bproc.utility.UndoAfterExecution():
# Select the surfaces, where the object should be sampled on
droppable_surface = bproc.object.slice_faces_with_normals(obj)
- Specify with objects to use to sample on. In this case, it’s “table” and “desk”.
- Then for each of those objects, the biggest surface is selected (e. g. top of the table) for sampling.
Front3DObjectSampling¶
surface_height_z = np.mean(surface_obj.get_bound_box(), axis=0)[2]
def sample_pose(obj: bproc.types.MeshObject):
# Sample the spheres location above the surface
obj.set_location(bproc.sampler.upper_region(
objects_to_sample_on=[surface_obj],
min_height=1,
max_height=4,
use_ray_trace_check=False
))
#Randomized rotation of the sampled object
obj.set_rotation_euler(np.random.uniform([0, 0, 0], [np.pi * 2, np.pi * 2, np.pi * 2]))
dropped_object_list = bproc.object.sample_poses_on_surface(sampling_obj, surface_obj, sample_pose,
min_distance=0.1, max_distance=10,
check_all_bb_corners_over_surface=False)
- Get the height of the sampling surface
- For every surface, the object is placed by
bproc.object.sample_poses_on_surface. - This also needs a pre-defined
sample_pose()function, where the sampling surface, as well as the minimum and maximum sampling height, are given. - It also sets the rotation of the sampled object.
Front3DObjectSamplingChecks¶
# get the minimum value of all eight corners and from that the Z value
min_coord_z = np.min(dropped_object.get_bound_box(local_coords=False), axis=0)[2]
# Check if object is on surface, otherwise delete object
remove_list = []
for index, dropped_object in enumerate(dropped_object_list):
# if distance is smaller than 5 cm
print(f"Object: {dropped_object.get_name()} has a diff of: {abs(min_coord_z - surface_height_z)}m to the surface")
if abs(min_coord_z - surface_height_z) > 0.05:
print("Delete this object, distance is above 0.05m")
dropped_object.delete()
remove_list.append(index)
- After running the physics we have to check if the sampled object is still on the surface.